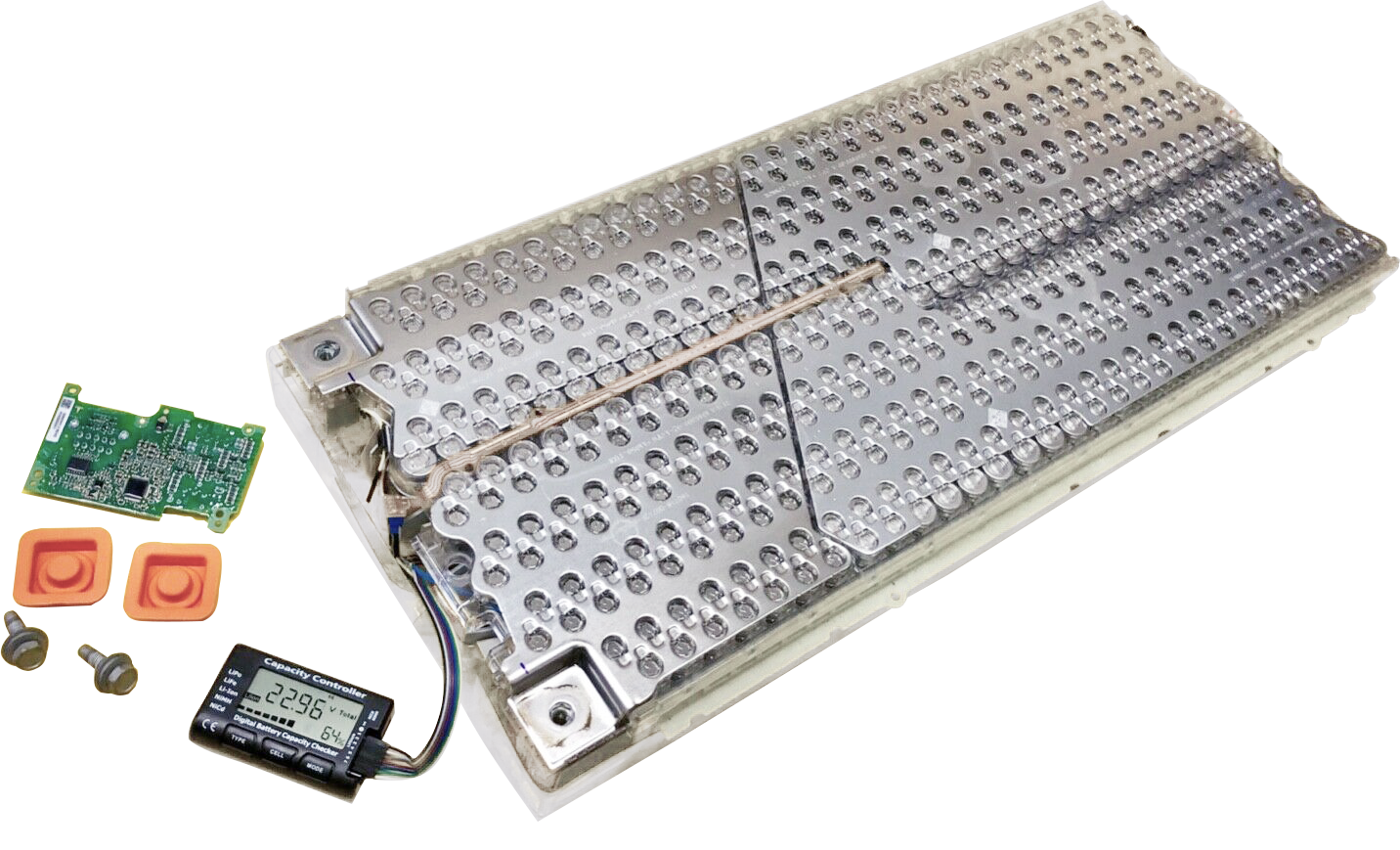
When it comes to battery modules, two other words often come to mind: battery cell, battery pack. In fact, battery is a generic term for all three, while battery cell, battery module and battery pack are different forms of batteries in different stages of application. The smallest of these units is the battery cell, several cells can form a module, several modules can form a battery pack by adding BMS and other management systems. Therefore, we can understand the battery module as an intermediate product between the battery cell and the battery pack. When multiple battery cells are packaged together in the same housing frame and linked to the outside through a uniform boundary, this makes up a battery module. It consists of a series-parallel combination of cells, the structure of which must play a role in supporting, fixing and protecting the cells. Whether it is able to fix the cell position and protect it from performance-damaging deformation, how to meet the temperature control of the cell, etc., will be the criteria for judging the merits of the battery module.
|
|
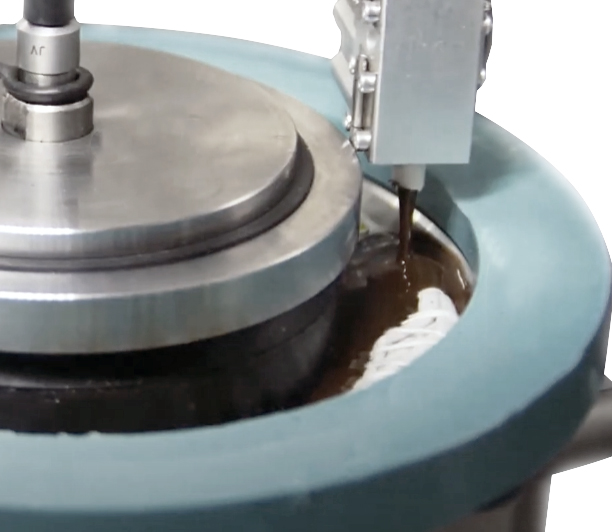
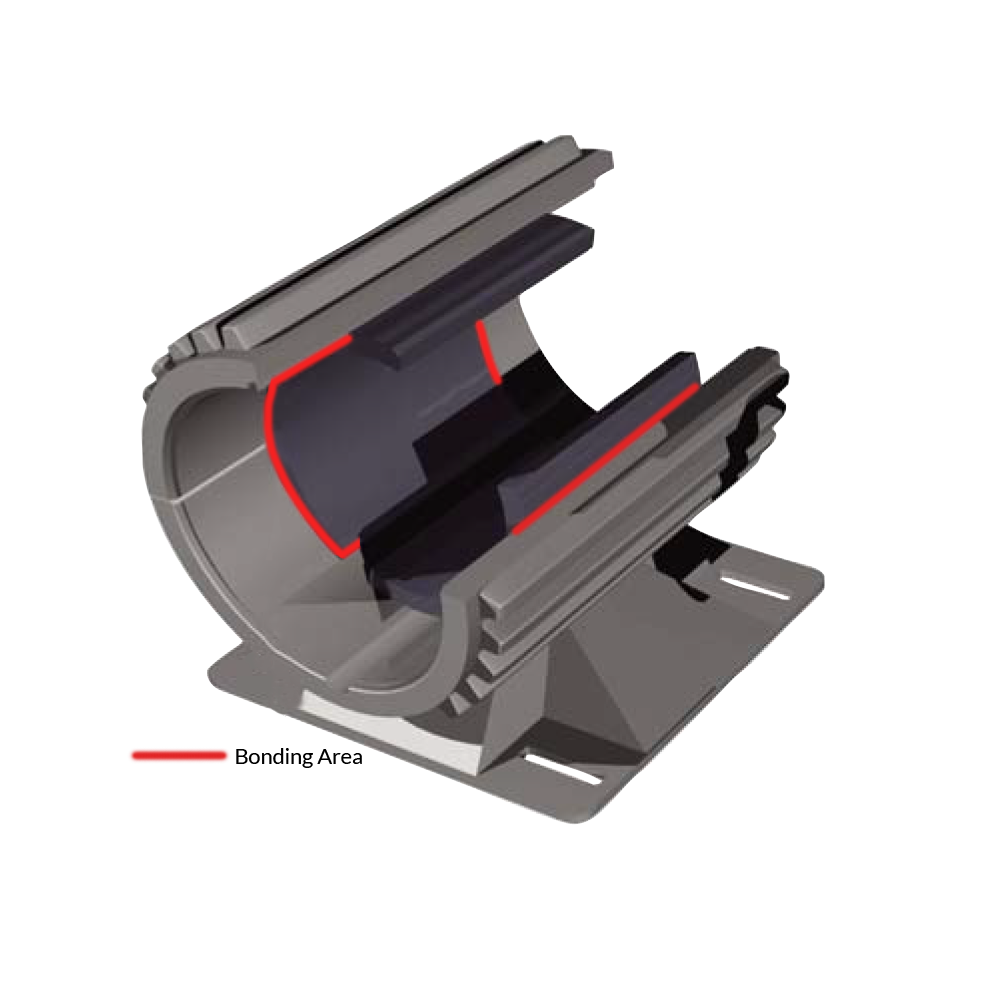
Battery Cell Bonding Battery Cell Assembly Process depends on the cell format and the individual manufacturer designs. They are manufactured in many sizes to fit the product. The most common shapes are cylindrical and rectangular (pouch and prismatic cell). While the use of either shape is dependent on the battery pack design, securing the cells into their larger battery modules or trays, takes different adhesive and dispensing approaches. |
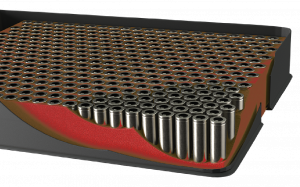 |
Encapsulation Foam One fundamental purpose of a battery is to pack as much power into as small a space as possible. This sounds simple, but as power density increases, new challenges arise. The denser a battery becomes, the more heat is generated in a smaller space, especially during a failure event. To overcome this challenge in the module assembly process, two-component materials such as silicone, silicone foam, epoxy, epoxy foam, and polyurethane foam are mixed and dispensed into the module to fill the spatial cavities between each cell. |
 |
Busbar for Battery Pack High-power EV battery is a combination of cells in series or parallel to achieve voltage ratings approaching 400V. The demand of connecting individual cells of about 1.5 to 2.0V requires a material good at both conducting and insulating rather than typically insulated cables. And that effective material is called BUSBAR – an electric conductor and ground plane separated by an insulator. |
 |
Threadlocker Mechanical locking devices (such as split washers, nylon nuts, flat washers) were invented to solve the common problem of loosening that happens in most threaded assemblies. The reality is that they don’t maintain clamp load as assemblies “locked” with these devices often loosen under vibration, thermal expansion and/or improper torque. |
 |
Temperature Sensor Temperature sensors are a key component in Li-Ion battery charging and safety. They provide critical temperature data required to keep the Li-Ion battery in optimum condition during the charging cycle. Careful management of temperature during charging prolongs battery life and avoids hazards inherent to Li-Ion batteries. |
 |
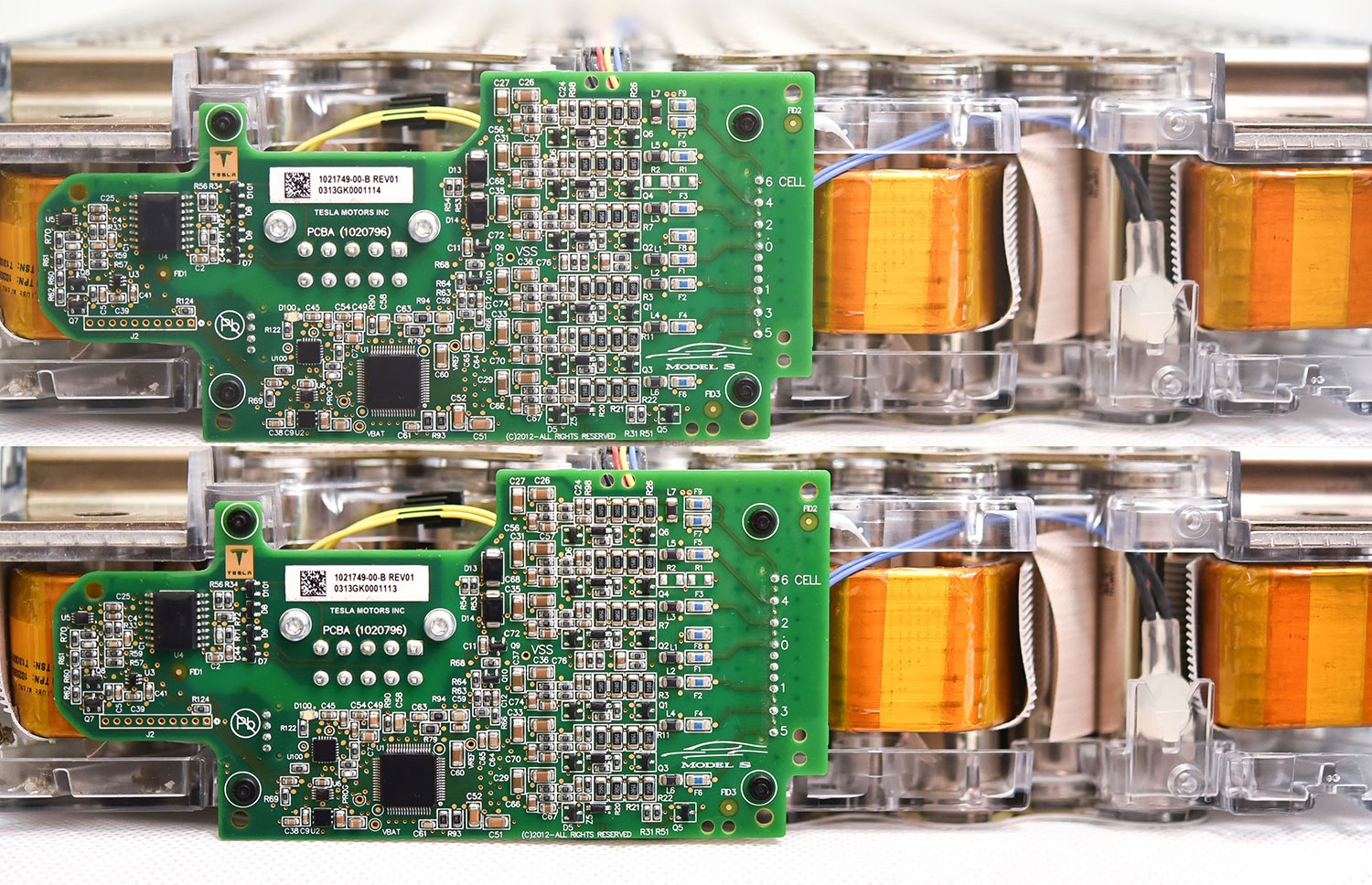
Battery Module Management BMU
|
Contact us for more information: