In conjunction with the development of wearable technologies, such as smartphones, AR/ VR glasses, smartwatches, and even interacting clothing, the advancement and widespread adoption of technology in PCBs have paralleled the rapid advances in semiconductor packaging technology, enabling industry professionals to invest in smaller and more efficient electronics.
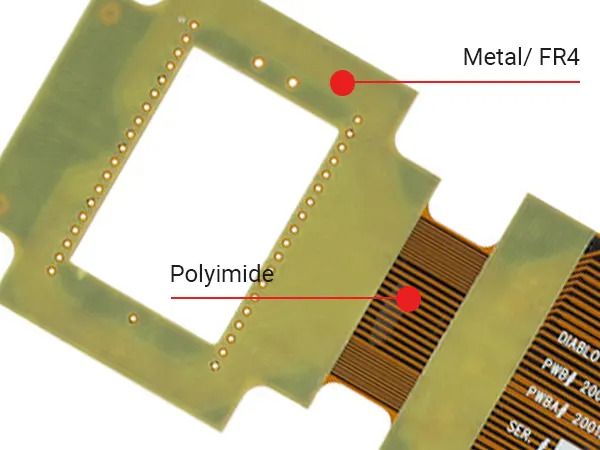
It’s also ushered in the era of formfitting medical devices capable of monitoring the wearer’s health via direct contact with the skin and smartphones using folding displays, among other technologies. To realize those devices, a new type of PCB needed to be developed, one that could stretch and warp beyond right angles. Engineers rose to the challenge to create flexible circuit boards using various techniques and materials, including polyimides, transparent polyester, and more.
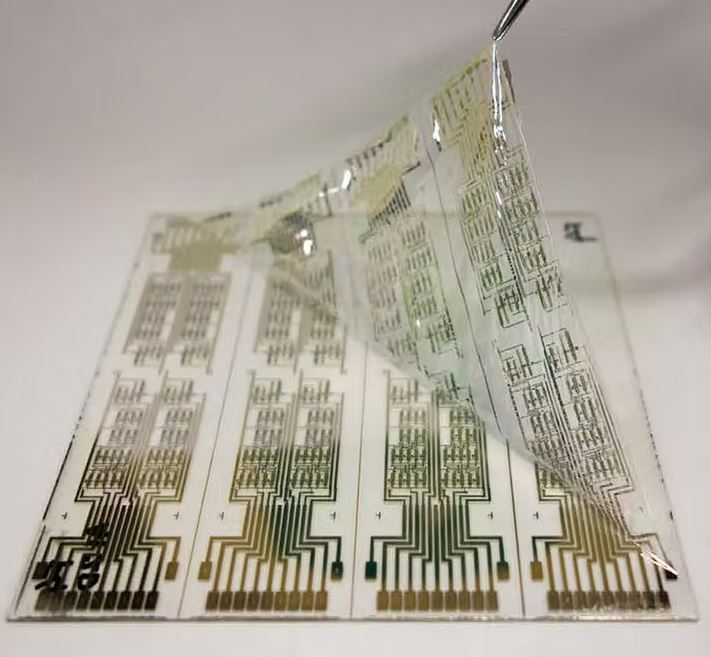
Type of Flexible PCBs
Manufacturers have adopted two types of malleable boards for today’s devices: flexible and rigid-flex PCBs.
Flexible PCBs
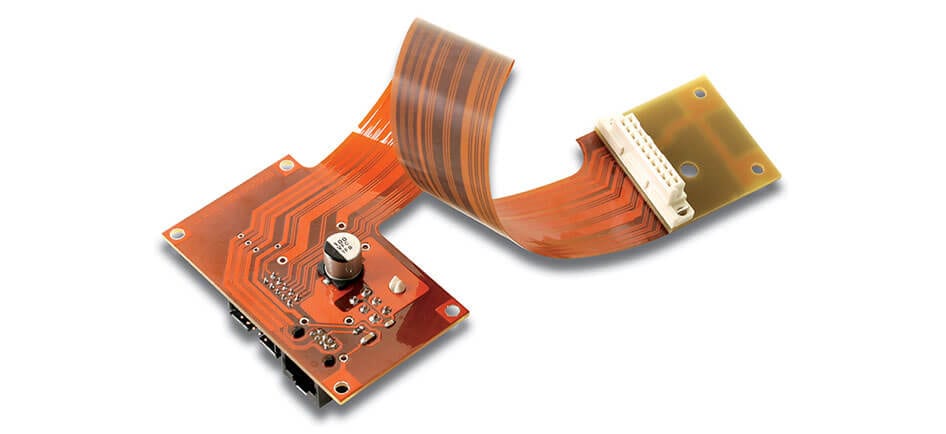
Or flexible circuit boards (FCBs), function similarly to their rigid counterparts, wherein the electronics are placed on a flexible substrate rather than a rigid platform. This makes it possible to form the electronics in different shapes and configurations instead of a planar surface. Based on the layer and configuration, these can be broken down into the two most common types mentioned earlier.
Rigid-flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs are hybrids, and boards that are both rigid and flexible to accommodate an arrangement of SMDs (surface-mounted devices, aka electronics) and connectors. In this configuration, the SMDs are mounted on a flexible substrate while the connectors reside on a rigid surface to maintain a stable connection and mitigate any damage from repeated use. The rigid-flex configuration also allows for increased capacity of SMDs because the connection terminations are placed on the rigid surface.

FPCB Bonding and Interconnecting Solutions
Depending on the type and design of flexible PCB, the bonding and assembly challenges will be different. In general, flex bonding is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The success of your intricate design requires a specific, reliable FPC bonding method. Our Flexible Circuitry Bonding Solutions give you the exact tape for your exact need — so you can create without limits.
Selection Guide
FPCB bonding tape will be selected after considering:
- Reliable bonding to different materials, from metal to plastics to polyimide.
- Tape enables fast processing.
- Tape meets your high-temperature processing needs.
- More die-cuttable options give you a more accurate edge profile.
- Anti-lifting tapes stay bonded even around curved or .bended surface designs.
Recommended Product List
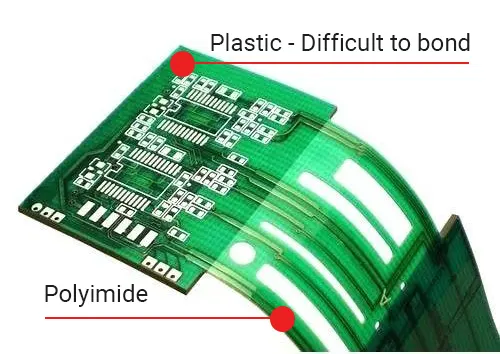
Robust solution for bonding hard-to-bond material (PC/ABS/PA/PET/powder-coated metal) to polyimide

Conductive FPC bonding
For more information about the bonding and reinforcement material in Flexible and Rigid PCB, please contact us:
Email: gluexpert@prostech.ph
Hotline: (+84) 984 695 398