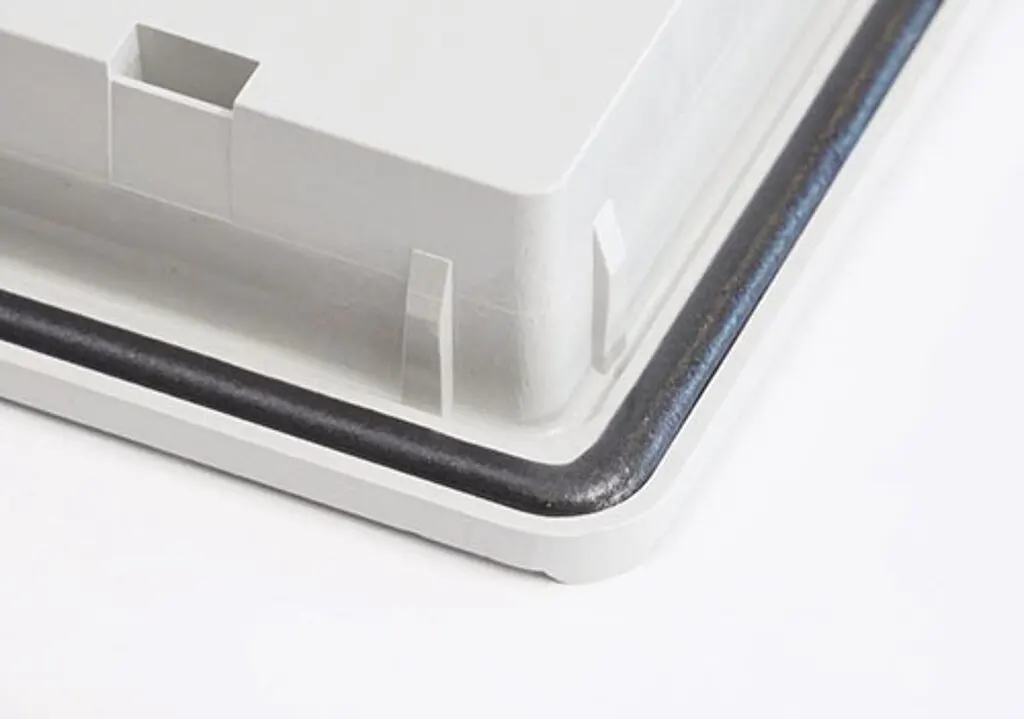
Adhesive bonding is used to fasten two surfaces together to produce a strong and reliable bond. These surfaces may be of the same nature or totally different. The “material” used to provide the bond may involve adhesives, 1-part or 2-part epoxies, or various other materials which bond by evaporation of a solvent or by curing a bonding agent with heat, pressure, and moisture or with a chemical reaction between the adhesive and the substrates.
There are some factors you should consider to achieve a good, reliable and strong bond.
• Bonding substrates
Different adhesives have varying bonding effects when used on different substrates and can achieve different bonding strengths and bond qualities. Some adhesives provide a rigid, fixed bond while others may provide a flexible bond which resists vibration. It is also very important to remember, when bonding different materials, that each material has a different “coefficient of expansion” when exposed to varying temperature. This means that, when exposed to heat, one material may expand faster then the other placing great stress on the adhesive. In this case, structural adhesives must be used. The compatibility between substrates and adhesives is very important. A good quality adhesive also needs to be applied onto clean surfaces of the substrate to provide the best performance. Removing oil, dirt, grease and other contaminants from the substrate surface, prior to bonding, is very important.
• Service temperature
There are many adhesives types, namely: acrylic based, silicone based, epoxy and solvent based adhesives. Since the bonding material becomes part of the end product, it must be reliable enough to work in same environment as the product. Selection of the correct chemical base adhesive, to ensure that the bond can withstand the working temperature of product, is extremely important.
• Working environment
In different working environments, the adhesives need different properties for chemical resistance, humidity and also to provide resistance to varying weather conditions. Naturally, the higher performance adhesives will be higher in price, but you must choose the correct adhesive with properties to support your products designs for product life and reliability.
The “characteristics” shown below provide the general information of the typical adhesives types.
For more details, and technical support, please fill in the form a side→
| Characteristic | |||||||
| Substrates Compatibility | Curing Time | Viscosity | Service Temperature | Chemical Resistance | Humidity and weather Resistance | ||
| Acrylic | Metal, Glass, Plastic, Wood | Fast | Medium | High | Good | Good | |
| Cyanoacrylate | Metal, Plastic, Rubber, Wood | Ultra-Fast | Low | Low | |||
| Hot Melt | Fabric, Paper, Plastic, Wood | Fast | Medium | Low | |||
| Silicone | Glass, Metal, Rubber | Slow | Medium, High | High | Good | Good | |
| Anaerobic | Metal, Plastic | Medium | Low | Low | |||
| Epoxy | Glass, Metal, Wood | Slow | Medium, High | High | Good | Good | |
| Polyurethane | Glass, Metal, Plastic, Rubber | Slow | Medium | High | Good | ||
| Solvent-Based | Paper, Rubber, Wood | Medium | Low, Medium | N/A | |||