Why need to add a Conformal Coating for Electrical Insulation purposes?
Electrical power rising trends

The growing dependence on electrical systems has led to a rise in the need for additional electric power. Various industries, including aerospace and automotive, are now prioritizing the replacement of mechanical systems with electrical alternatives in order to enhance efficiency, increase reliability, reduce maintenance expenses, and simplify the overall system.
High power & voltage electrical devices
To mitigate the loss of electric energy during generation and transmission at low voltages, it is recommended to increase the operating voltage level. This approach enables the transmission of higher amounts of electric power through systems without requiring any adjustment to conductors’ ampacity.
The entire insulation system experiences greater electrical strain with the rise in operational voltage.
Insulation failure, breakdown, or partial discharges (PD) in power systems can be caused by moderate levels of stress on the insulators.
To handle the heightened operational voltage level, extra conductor clearance or more insulation is necessary.
When the tradition insulation layer doesn’t work any more.
The electrical or electronic systems rely on printed circuit boards (PCBs) as their foundation and these boards face various types of stress such as mechanical, thermal, environmental, and electrical.
To protect PCB in harsh environmental conditions and increase its durability, a 25 – 250-μm thick layer of insulation functioned conformal coating is usually applied on PCB surface.
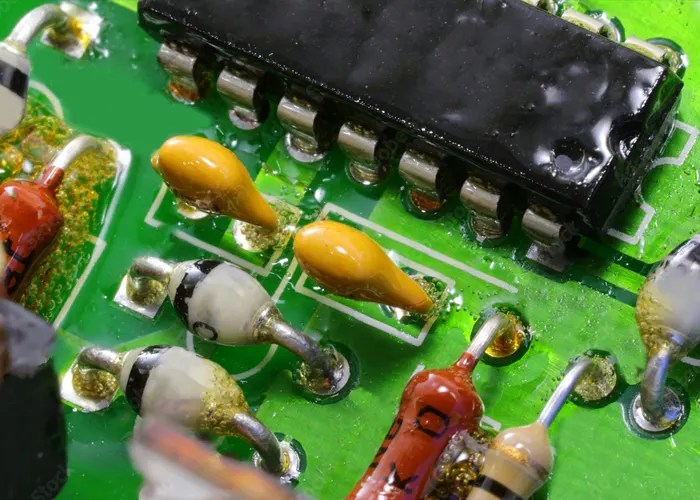

Depending on the PCB application, coating insulation mainly protects boards from one or more of the following failures due to operation in a harsh environment:
- Short circuit or current leakage between electrical paths or joints
- Arcing, corona discharge, and PD in high voltage assemblies
- Corrosion and degradation of traces on the board
- Solder joints fatigue failure
How to evaluate the insulation performance of conformal coating?
The criteria for determining the acceptability of a PCB are dependent on the intended use of the assembly. Different requirements apply to military, telecommunication, and consumer products. In addition, certain acceptance standards are at the discretion of the manufacturer and are based on factors such as product quality, lifespan, and company reputation.
The IPC-CC-830B & MIL-I-46058C are the current industry-approved standards for determining the acceptability of electronic assemblies.
IPC Standard Tests
| Appearance | Completed |
| Flourescence | Completed |
| Thickness | Completed |
| Flexibility | Completed |
| Dielectric Withstanding Voltage | Completed |
| Moisture and Insulation Resistance | Completed |
| Thermal Shock | Completed |
| Temperature and Humidity Aging | Completed |







